| Analysis and design tutorials | Analysis and design assignments | Prototypes | Exam 1 | Exam 2 | Questions and assessment |
CSD EXA1: midterm exam examples and solution ideas |
2425Q2
Problem 1
1. How to perform bitwise logic operations and arithmetic calculations using integers is presented in explained in L4.2. This Lab 4.2 shows another example of a 9-bit ALU.
2. General ALU architecture is explained in L4.2.
3. This P4 present an arithmetic circuit for integers.
4. A similar design is proposed in Lab 3.
Problem 2
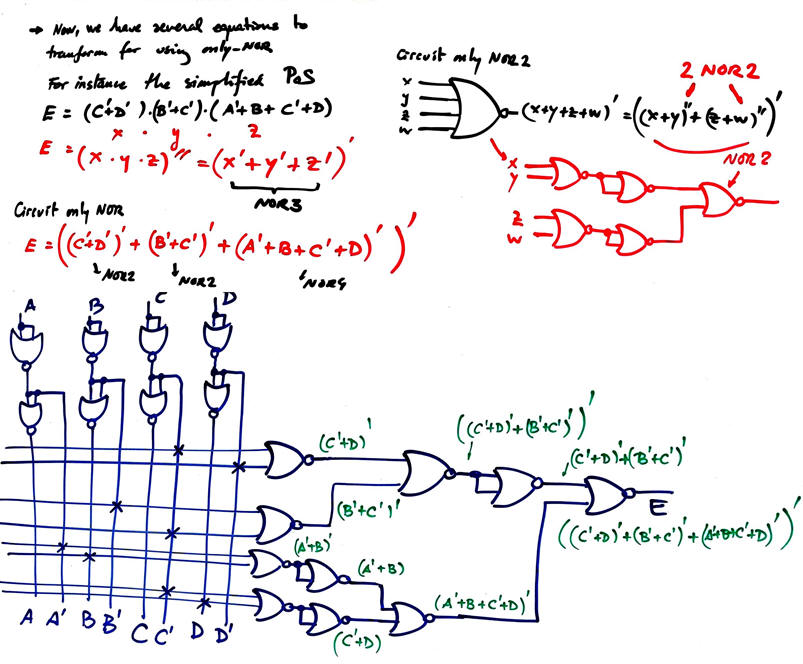
1. This sketch below shows a possible solution. This "Circuit_E.pdsprj" Proteus can be used to check the truth table.
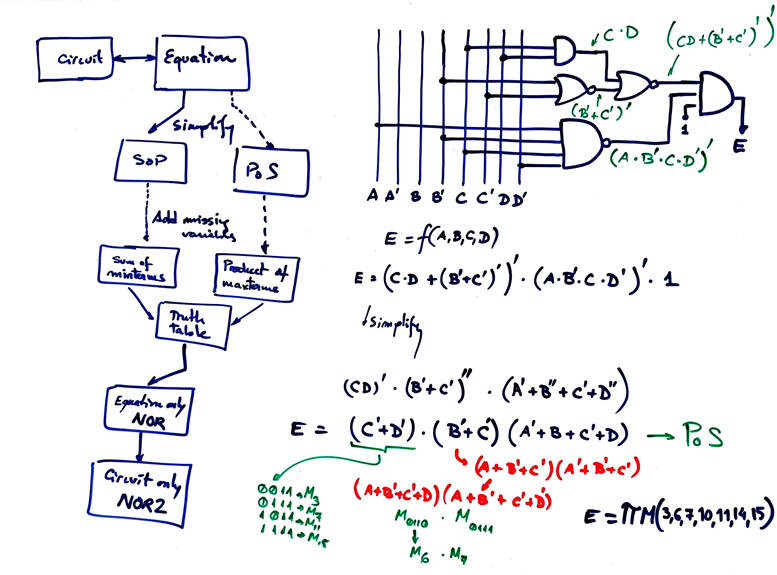
2. Ideas on power consumption and circuit's propagation delay are found in L4.3.
3. The sketch below shows one of the many possible circuits based on only-NOR2
Problem 3 - Problem 4
Examples of code converters from P2.
How to drive LED is found in L2.4 and basic electrical characteristics in L1.6.
MoM and MoD is explained in L3.3.
VHLD circuits using plan B can be found in many product examples, starting in this lectureL2.2.
Problem 5
From the D1.13 project. Basically here we ask about timing diagrams (specifications) and proposed internal planning. Try to obtain signal values for the given operands.
Problem 6
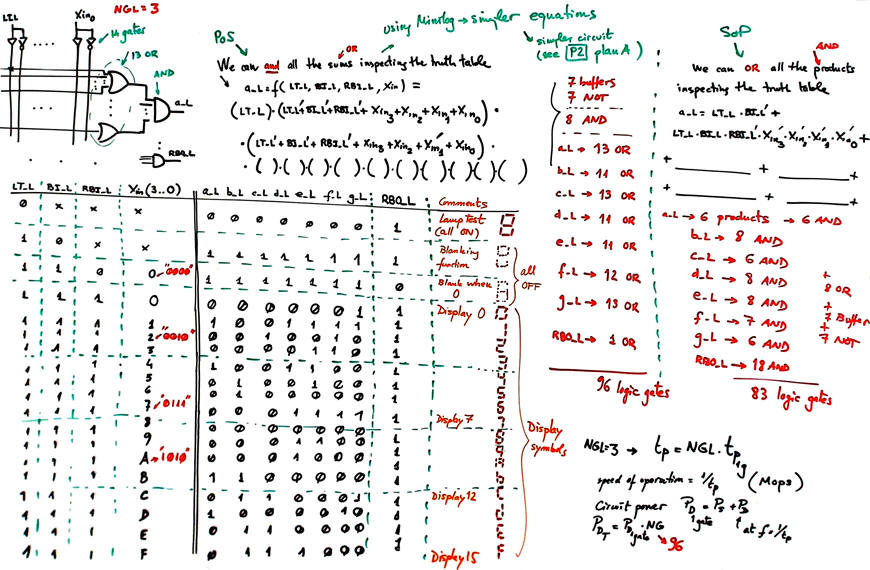
Get ideas from this P2 highlighted project. The sketch below shows how to count gates simply inspecting the truth table. Logically, applying Minilog will minimise the number of gates required to implement such circuit. A good exercise is to complete with LT_L, RBI_L and RBO_L the Hex_7seg_decoder Hex_7seg_decoder truth table ready to be used in Minilog to extract SoP or PoS. It will be the plan A version of this Dec_hex_7seg tutorial.