Lecture 3 |
L2.3: Designing standard logic circuits. VHDL: Decoders and encoders [P2] Flat (single VHDL file) plans: structural plan A / behavioural plan B |
[2 Mar] |
1.7.4. Binary decoder
1.7.4.1. Dec_3_8, Dec_4_16
Discussing binary decoder basics and specifications rec.. From our concept map: 1) Symbol, (2) truth table or equations, (3) timing diagram, (4) commercial chip, (5) internal design (Plan A, B, C1 or C2), (6) how to expand them (Plan C2 in P3)?
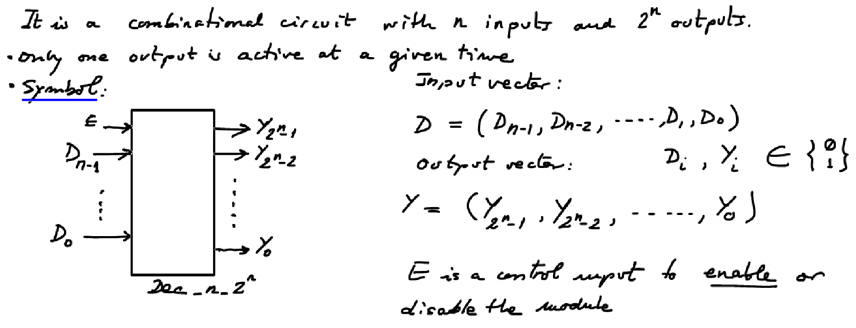 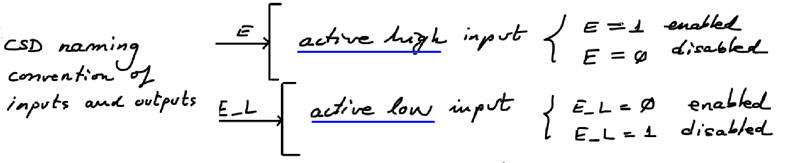 |
| Fig. 1. Generic binary decoder symbol. |
Fig. 2 shown the symbol and truth table when n = 3, it is a Dec_3_8 device.
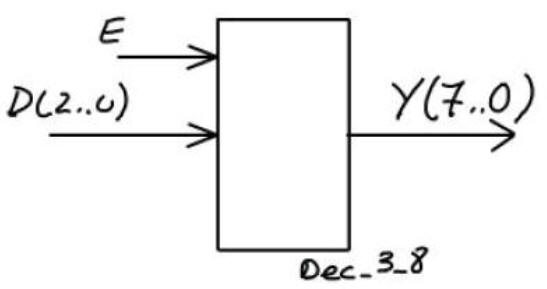  |
| Fig. 2. Dec_3_8 truth table. |
1.7.4.2. Design examples
- Plan A. This tutorial is the complete design using VHDL tools of the decoder Dec_3_8 using equations.
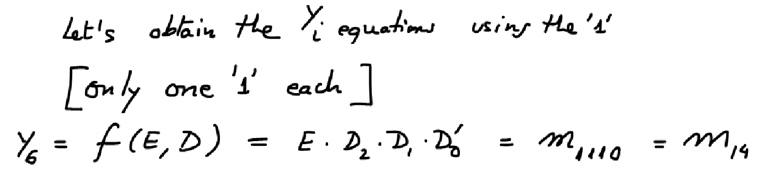 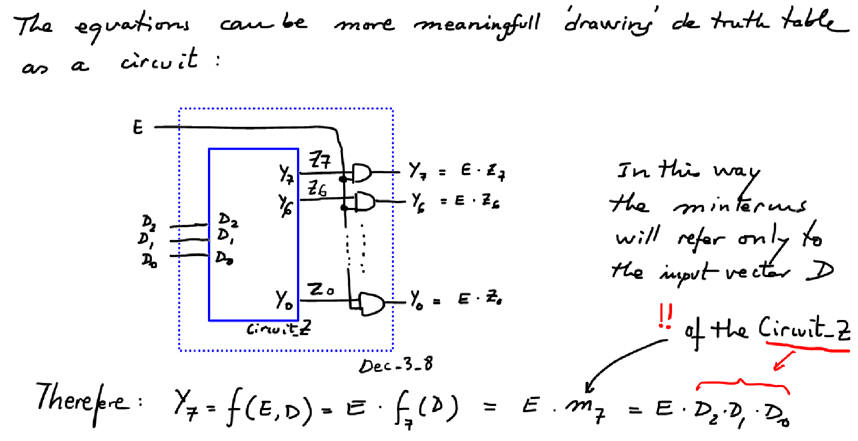  |
| Fig. 3. Structural equations inferred inspecting the truth table. |
Finally, we can draw this eight equations based on canonical minterms as represented in Fig. 4.
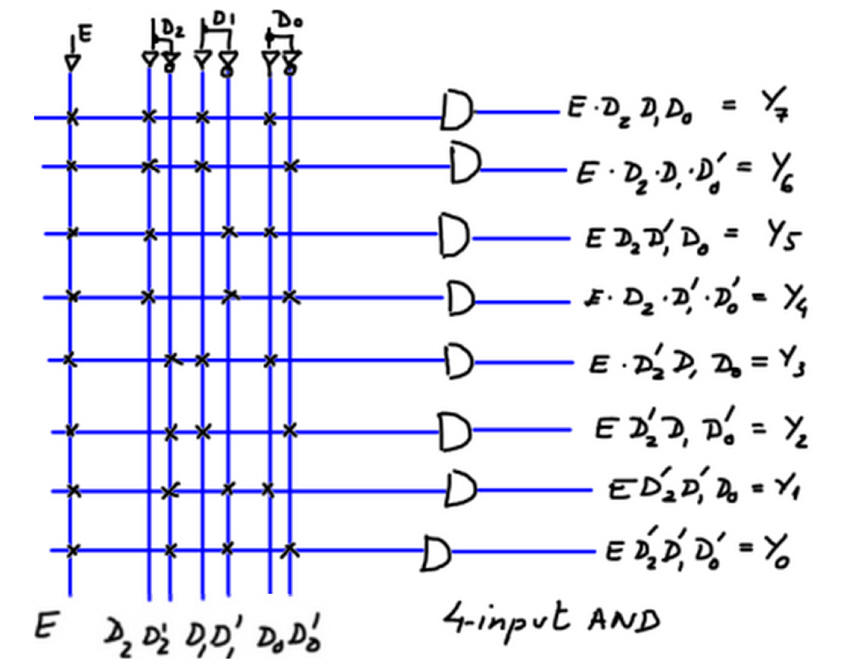 |
| Fig. 4. Circuit based on minterms. |
- Plan B. This tutorial is the complete design using VHDL tools of the decoder Dec_3_8 using the truth table, algorithm flowchart or any other high-level interpretation.
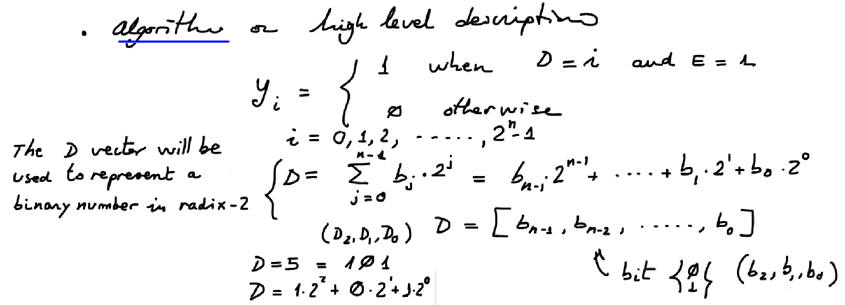 |
| Fig. 5. Circuit algorithm. |
1.7.4.3. Decoder expansion circuits (plan C2)
1.7.4.4. Commercial chips
74HCT138, etc.
1.7.5. Binary encoders (priority high)
1.7.5.1. Enc_8_3, Enc_10_4
The symbol for an Enc_8_3 is represented in Fig. 6 and its truth table in Fig. 7.
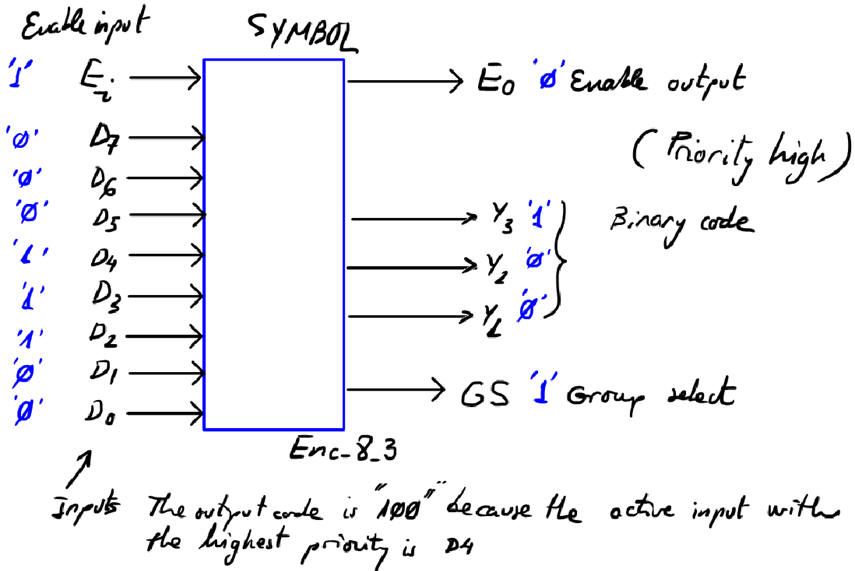 |
| Fig. 6. Circuit Enc_8_3. |
This truth table is 512 rows long. It can be written in a compact form using don't care terms as shownin Fig. 7.
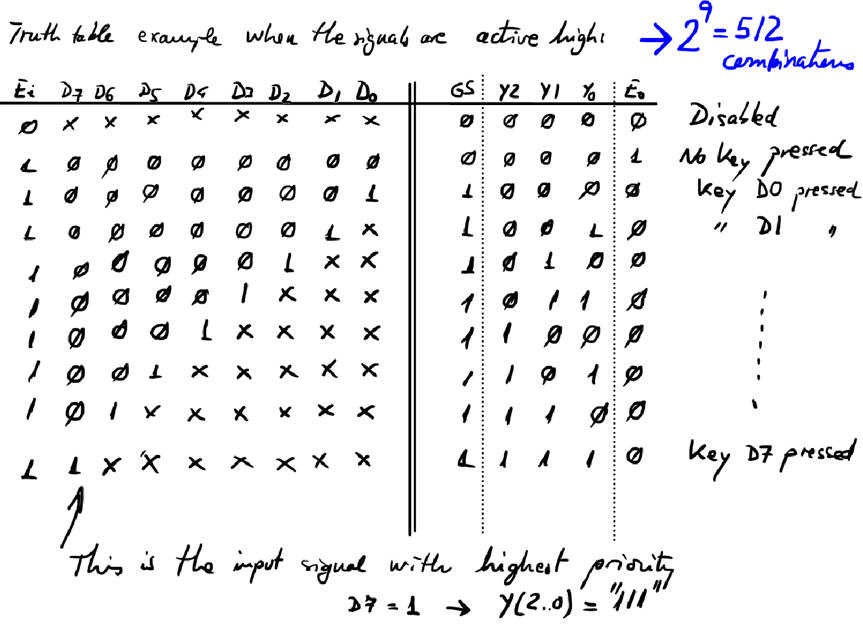 |
| Fig. 7. Enc_8_3 truth table. |
And an example of timing diagram is represented in Fig. 8.
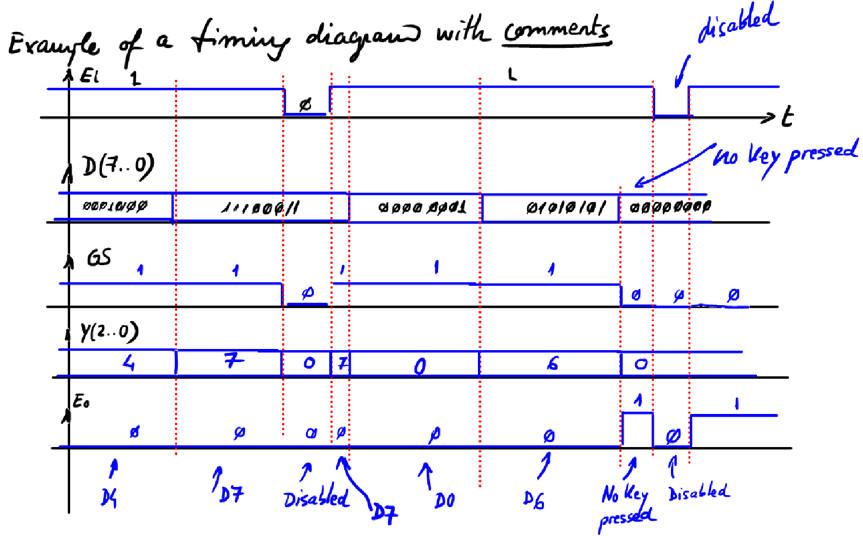 |
| Fig. 8. Enc_8_3 timing diagram example. |
We can start thinking now on design plans, for instance Plan A trying to deduce some equations.
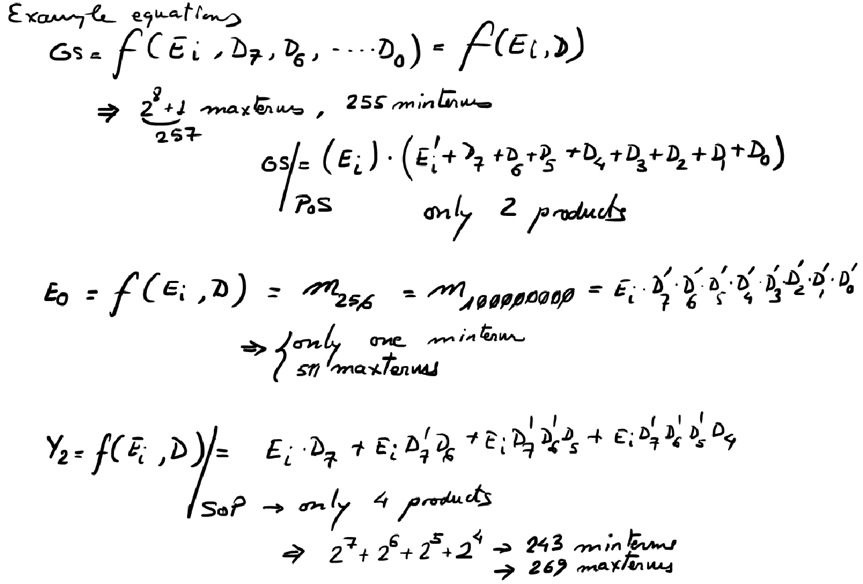  |
| Fig. 9. Some equations after exploring the truth table. Using Minilog will generate the complete list of output functions in SoP or PoS form, ready for VHDL translation as Enc_8_3.vhd source file. |
1.7.5.2. Design examples
- Plan A. Discussion of the binary encoder Enc_10_4 using equations.
- Plan B. Discussion of the binary encoder Enc_10_4 using the truth table, algorithm or any other high-level interpretation.
1.7.5.3. Encoder expansion circuits (plan C2)
1.7.5.4. Commercial chips
74LS148, 74LS147, CMOS 4532B, etc.
Activity #1: Invent an Enc_8_3 with priority-low using our VHDL tools adapting the symbol and its truth table from the commercial circuit 74LS148.


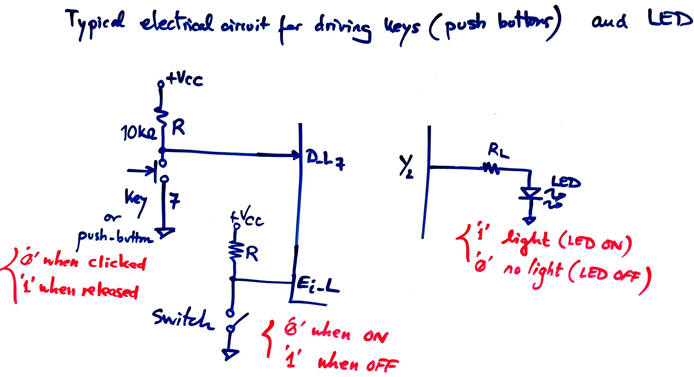
Priority-low means that when clicking several keys at the same time, the circuit generates the binary radix-2 code corresponding to the lowest number. For instance, if you click simultaneously keys 7, 5 and 2, the encoded output is "010".
Use one of these plans:
- Plan A equations. Use Minilog to obtain SoP or PoS.
Project location: C:\CSD\P2\Enc_8_3\PlanA\(files)
- Plan B high-level description. Draw a flowchart or an schematic to translate the circuit's truth table into VHDL.
Project location: C:\CSD\P2\Enc_8_3\PlanB\(files)
Activity #2: Adapt, using logic gates if necessary, the 74HCT138 commercial chip to the symbol in picture Fig. 2.


