Lecture 3 |
L1.3: Circuit analysis using Boole's algebra (method I) P1 Analysis. Example Circuit_W (a section of Circuit_C) |
[16 Feb] |
1.4. Analysis concept map: several methods for analysing simple combinational circuits
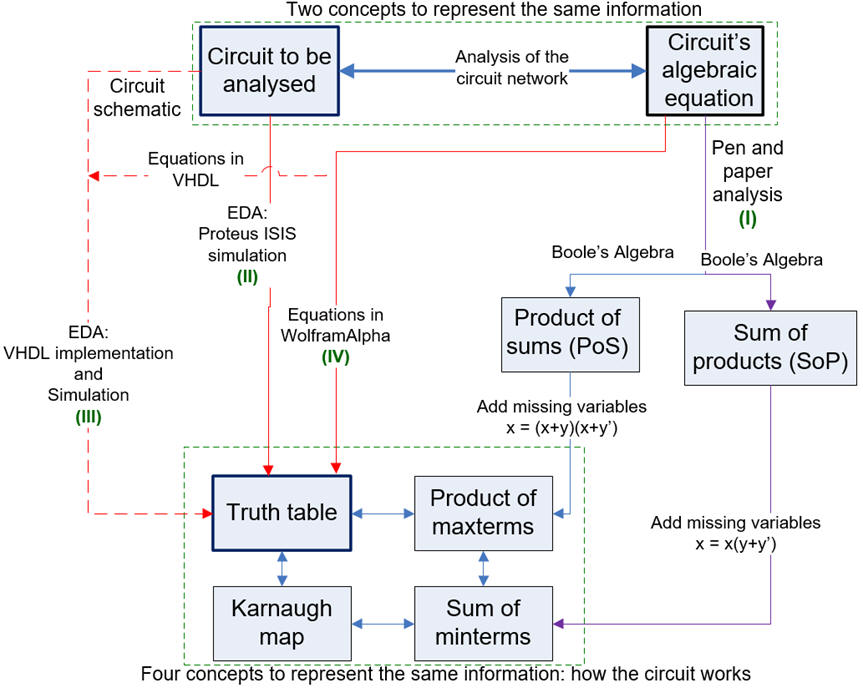 |
| Fig. 1. General analysis map proposing several methods to deduce the circuit's truth table. |
1.4.1. Method I: Pen & paper analysis using Boolean algebra
1.4.3.1. Properties of Boolean functions
1.4.3.2. Duality principle, De Morgan's laws
1.4.3.3. Product of sums (PoS)
1.4.3.4. Sum of products (SoP)
1.4.3.5. Any type of equation or non-standard forms
Step 2 on analysing a simpler circuit:
|
Project tutorial #1: Analysis of the Circuit_W |
1.4.2. Method II: Proteus simulation for truth tables and deducing logic circuits (Lab1_1)
1.4.4. Method IV: WolframAlpha engine for calculating truth tables and deducing logic circuits (Lab1_1)
1.4.3. Method III: Analysis using synthesis and simulation EDA tools (Lab1_2)
Activity #1: From the PoS simplified expression obtained above,
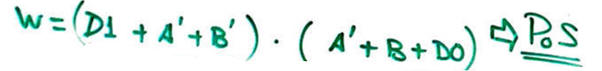
develop the equivalent SoP and convert each product into minterms. Check the final truth table.
These notes are an indication on how to organise this analysis project in our CSD style:
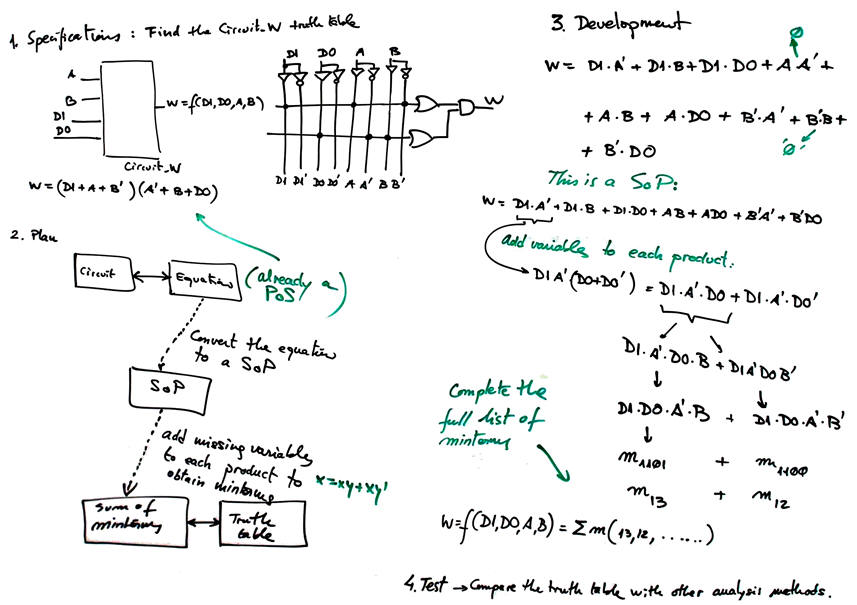
Activity #2: Step 3 on applying again everything to the Circuit_C
Repeat and apply all these method I analysis concepts to Circuit_C proposed in P1 as highlighted project.
Activity #3: This is another example activity that can be solved after this lecture.
Repeat and apply all these method I analysis concepts to Circuit_T proposed below.

Activity #4: Analyse the following circuit using method I to deduce its truth table.
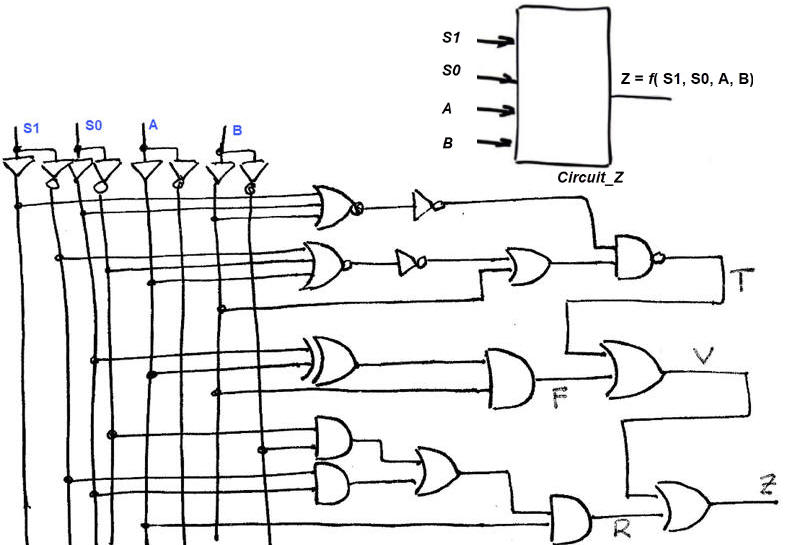
You already deduced its equation in L1.2 Activity #2.


