L10. 1. FSM adaptation. External interrupts (INT) [P10] FSM design programming in C. Detecting events (signal edges) using external interrupts. |
[18 May] |
3.5. FSM implementation in C language
3.5.1. Specifications
3.5.1.1. FSM concept adaptation to µC.
How to generate a CLK-like synchronisation signal when executing software? How to synchronise operations like state transitions in a FSM each time an active CLK edge is detected as it was done in Chapter 2? We will answer these important questions using an external CLK signal or overflow flags from embedded peripheral such TMR0 or TMR2 to generate interrupts to the main program. Therefore, we will solve two main ideas:
- Adapting a FSM in software, as a way to implement the same applications proposed in Chapter 2.
- Detecting signal transitions or events such rising or falling edges by means of interrupts to the main program.
Such events will trigger hardware flags (INT0IF, INT1IF or INT2IF) that will the used in the interrupt service routine ISR() f to set our software flags (var_flag) that will run the state diagram.
In addition to external pins, many other peripheral subsystems (timers, A/D, USART, analogue comparators, etc.) will be able to trigger interrupt events.
Fig. 1 shows Chapter 2 FSM architecture as it was studied and applied in many applications to solve sequential systems.
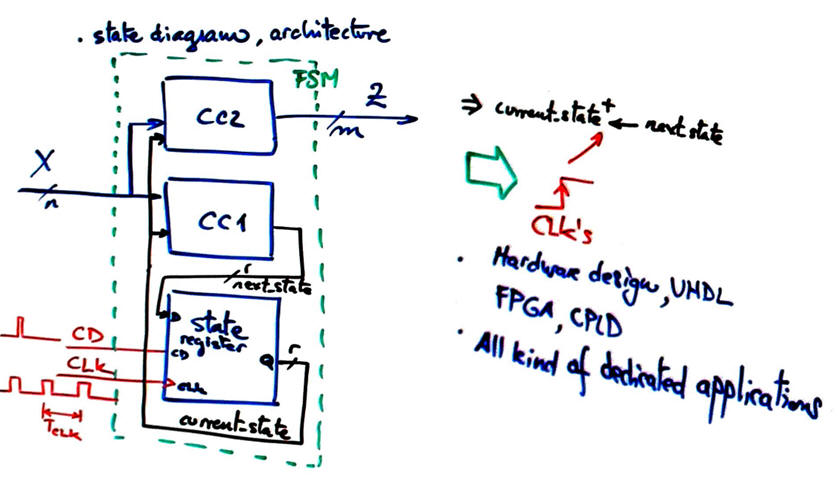 |
| Fig 1. FSM architecture. |
Now, we propose to adapt the same architecture to software environment as shown in Fig. 2.
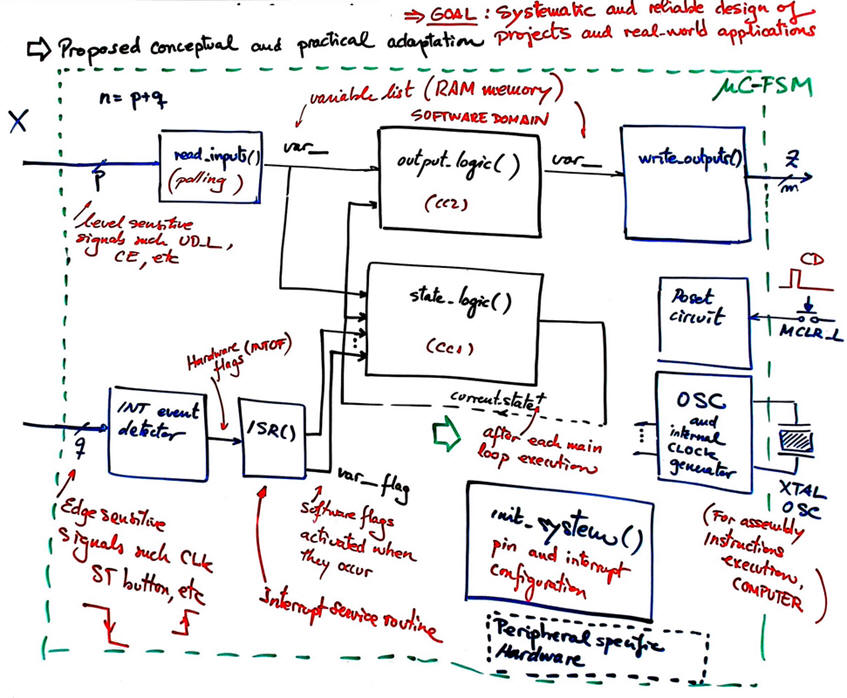 |
| Fig 1. FSM adaptation rec: interrupts will allow detection of events (signal edges) and will make it possible to run state diagrams systematically programmed in C, as we did in Chapter 2. |
Current state as RAM memory variable.
3.5.1.2. CLK interface using interrupts
How to detect signal edges.
3.5.2. Planning
3.5.2.1. Hardware-software diagram
3.5.2.2. Interrupts: interrupt service routine ISR(). External event detection (CLK and push-button interface)
The key concept of external interrupt (INT) to the main program. Pay attention to the idea of external interrupt to detect a signal edge at the input pins and how they are handled by the μC in hardware (INT0IF, INT0IE, GIE) and once acknowledged at the ISR() software (Var_CLK_flag). The concept of the interrupt vector to execute the ISR() special function. The concepts of nested interrupts, stack memory and stack overflow.
Enabling and disabling interrupts in init_system().
3.5.2.3. output_logic() and write_outputs().
3.5.2.4. state_logic() and read_imputs()
3.5.3. Development & testing
References:
- Carmely, T., Using finite state machines to design software, EDN, March 30, 2009
- Bergfeld, D., Software design of state machines , Embedded.com, April 16, 2019
- This is how Microchip explains the idea of implementing control flow in structured programs by means of a sequence of task. Each one of them may be a FSM. "Getting Started with PIC16F1xxx MCUs using MCC and State Machines", Microchip University Course. Reference on program control flow strategies.
Activity #1: Let us imagine a click duration meter. An external time-base oscillator (TB) is fixing the time resolution. If n bits are used to output the measurement, we can count up to QMAX = 2^n - 1.

Plan it as in Chapter 2, with a FSM and a datapath to discuss the kind of circuits that such device will contain. The FSM will allow counting only when the push-button is pressed. The counter's overflow signal means that the duration of the click is over range.


Adapt the architecture to µC. Detect the duration of the active-low push-button PB_L click using configuring the external interrupt (INT1) to detect both, positive and negative signal edges. Use another external interrupt (INT0) to detect rising edges from the external CLK (time base). What be be the list of RAM variables required? How to configure int_system(), what is the software flowchart for ISR()? What kind of processing the FSM can do?
You can proceed to complete the project and run and test it in Proteus.
A similar circuit may be used to measure the speed of a vehicle. Two inductive sensors embedded in the tarmac generate the start and stop pulses for counting.


