|
CLK circuits |
RC, quartz crystal and other simple digital oscillators
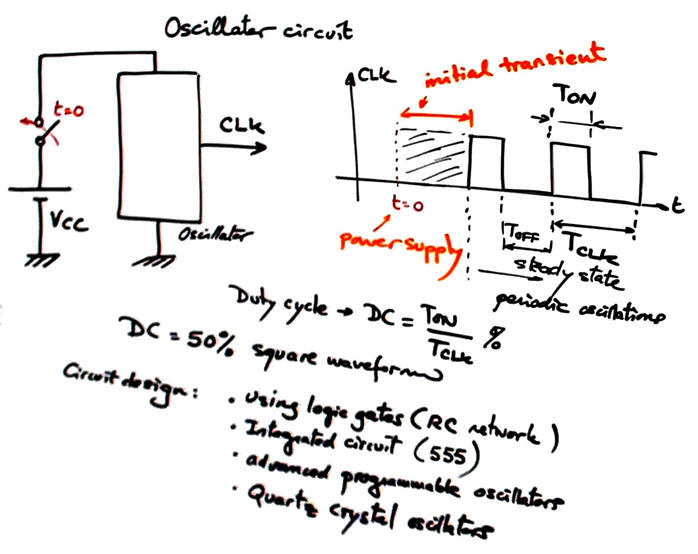
The idea of an oscillator circuit is represented in Fig. 1. You simply have to power the circuit and it starts generating a periodic rectangular waveform. The key parameters are voltage levels for '0' and '1' and period TCLK. A good question for these devices that will determine which circuits and components to use for a given application is: how accurate is TCLK?
 |
|
Fig. 1. Symbol and concept of an oscillator circuit. |
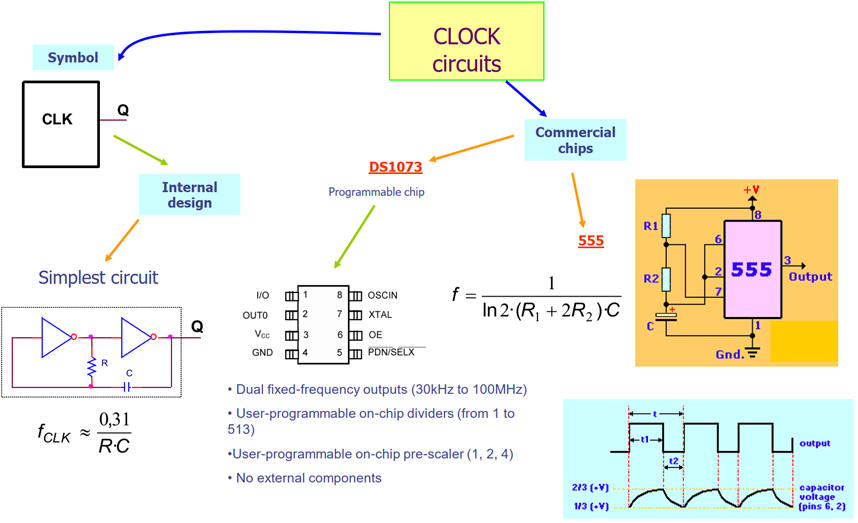
Fig. 2 shows how oscillators can be invented from simple NOT gates to dedicated integrated circuits.
 |
|
Fig. 2. Initial idea on simple digital oscillators. |
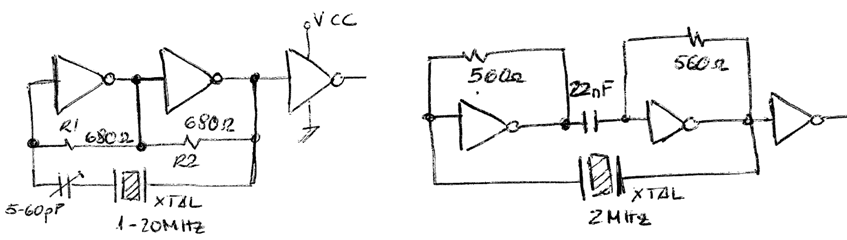
The idea of oscillation based on NOT gates.
2.3.2. CLK Circuits
2.3.2.1. RC circuit
RC oscillator
Fig. 3 shows a circuit that will freely oscillate using the sextuple 4069UB chip. If VDD = 5V, calculate its oscillation frequency. Demonstrate how it works simulating the circuit in Proteus and compare results. This is the circuit RC_CLK in Proteus.
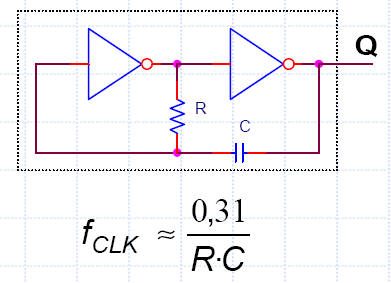 |
Fig. 3. Typical RC oscillator. Time constant determines the circuit oscillation frequency along with technology values associated with low and high logic margins. |
The analysis in Fig. 4 shows how to deduce its oscillation frequency.
| oscillation frequency |
Fig. 4. Analysis for deducing oscillation frequency. |
The circuit represented in Fig. 5 is a typical application to generate a sound wave (ref. Rudolf F. Graf, The encyclopedia of electronic circuits, volume 6).
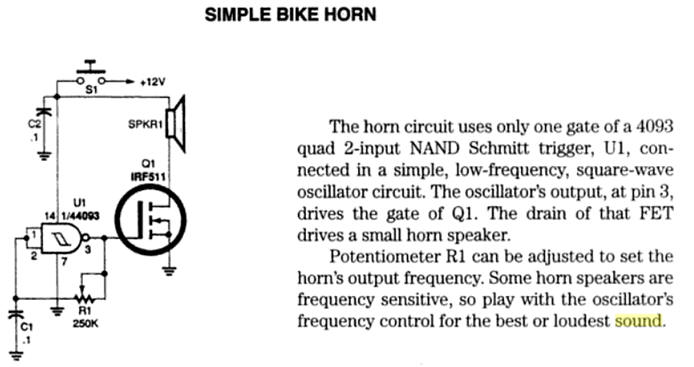 |
| Fig. 5. Oscillator for a bike horn. It oscillates when clicking the button S1 that connects the power supply. Try to simulate the circuit using Proteus and be aware on how the audible frequency can be adjusted using R1. |
2.3.2.2. Integrated circuit 555 oscillator
Oscillator based on 555 chip
Fig. 6 shows the typical oscillator schematic from the 555 IC datasheet where R-C components determine the frequency of oscillation with higher precision than in previous circuits based on logic gates. This is the circuit 555_oscillator.pdsprj in Proteus for experimentation. Many more functions can be implemented using this classic integrated circuit: PWM, PPM, timer, ramp and pulse generator, time delay, etc.
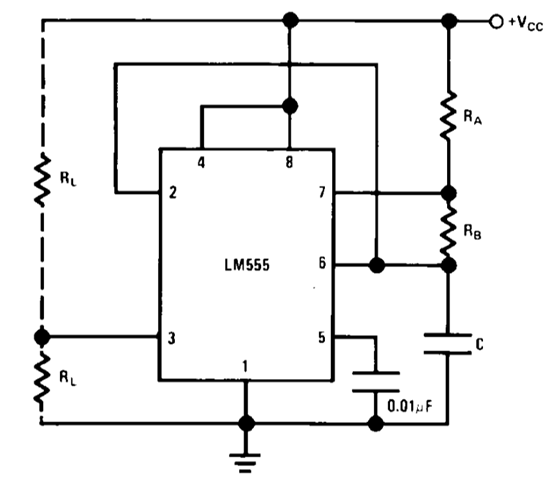 |
Fig. 6. Typical 555 rectangular wave oscillator. |
Fig. 7 shows the 555 functional blocks and their mode of operation.
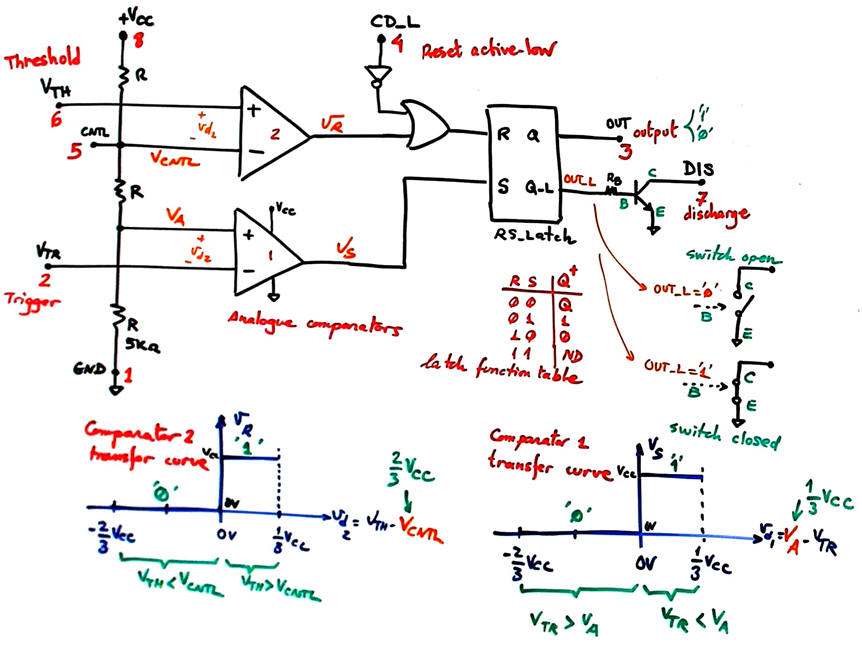 |
| Fig. 7. Analysis for deducing oscillation frequency. |
Therefore, when the 555 is connected as in Fig. 6 to an external R-C network allows as to calculate its oscillation frequency fOUT in several steps imagining the external capacitor initially discharged. C is charged through RA+RB and discharged through RA.
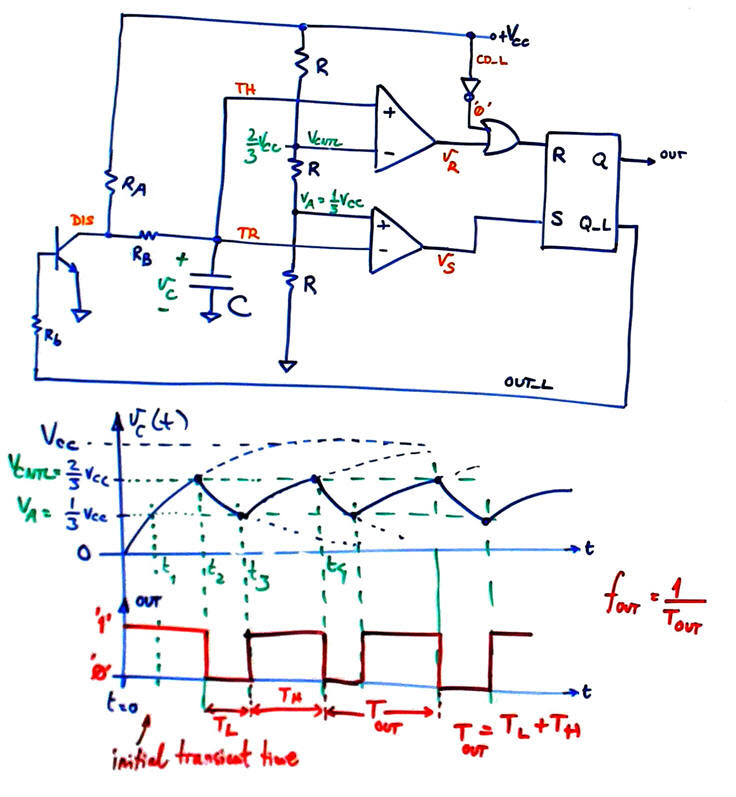 |
| Fig. 8. Periodic oscillations after the initial transient time up to t = t1. The analogue comparators and the voltage divider keeps the capacitor voltage charging and discharging between clear boundaries VC(t2) = (1/3)VCC and VC(t3) = (2/3)VCC. |
Therefore, we can calculate the TL and TH to deduce the oscillation frequency.
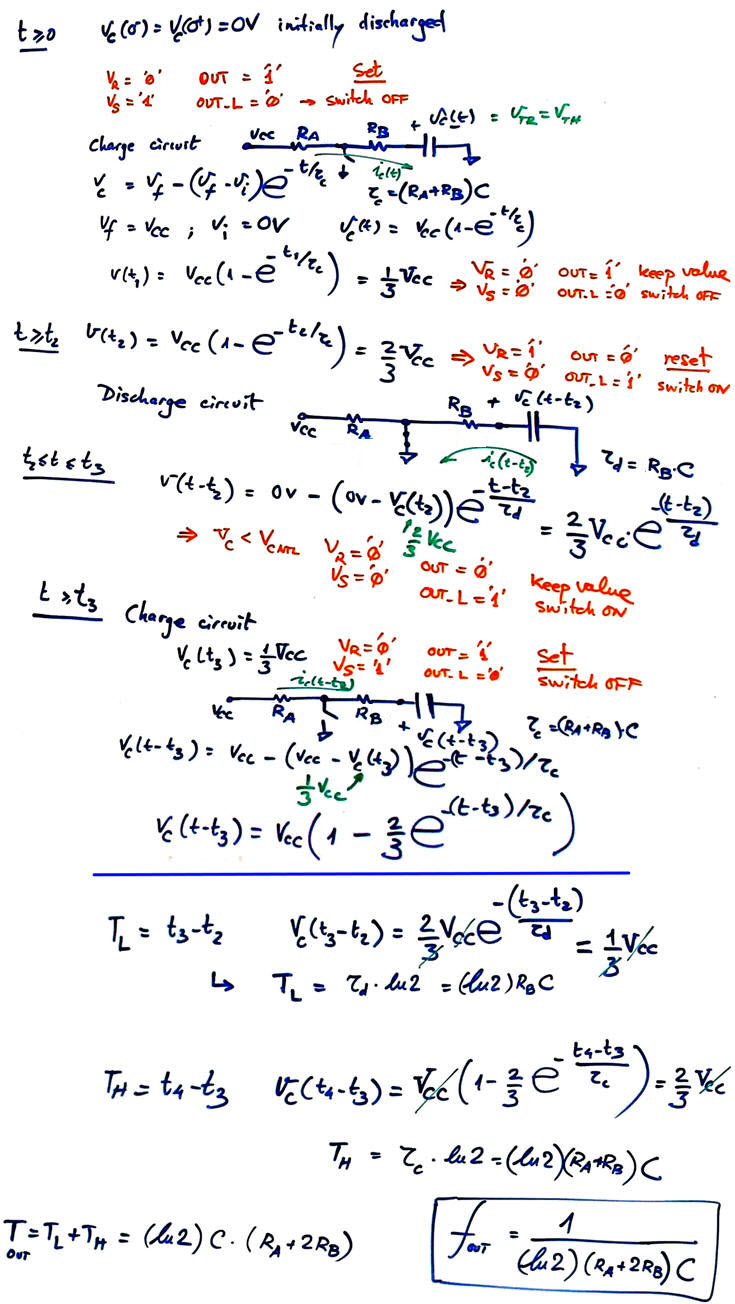 |
| Fig. 9. Capacitor voltage evolution through the two time variant circuits for charging and discharging. Period TOUT = TL + TH calculation. Adjusting the resistor values we can fix the rectangular waveform shape duty cycle, and using the C value we can establish the oscillation frequency. |
Some modifications on this basic circuit allows square waveforms and also PWM. For example, in this tutorial capstone project on the design of a lamp dimmer, you can see how the fixed resistors RA and RB are replaced by a potentiometer.
Another interesting programmable CLK chips is the classic DS1073 from Dallas.
2.3.2.3. Quartz crystal oscillator
Quartz crystal oscillator
The typical quartz crystal oscillator will lose one second every couple of years, which makes it very convenient for all kind of real-time practical applications. Fig. 8 shows typical crystal oscillators. Wikipedia entry on crystal oscillators.
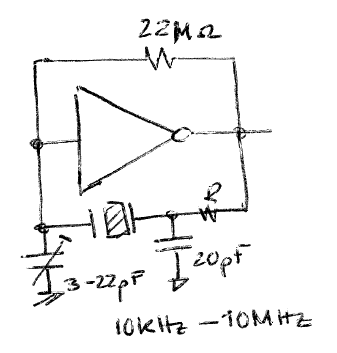 |
Fig. 8. Example oscillator using a quartz crystal and a simple logic gate. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
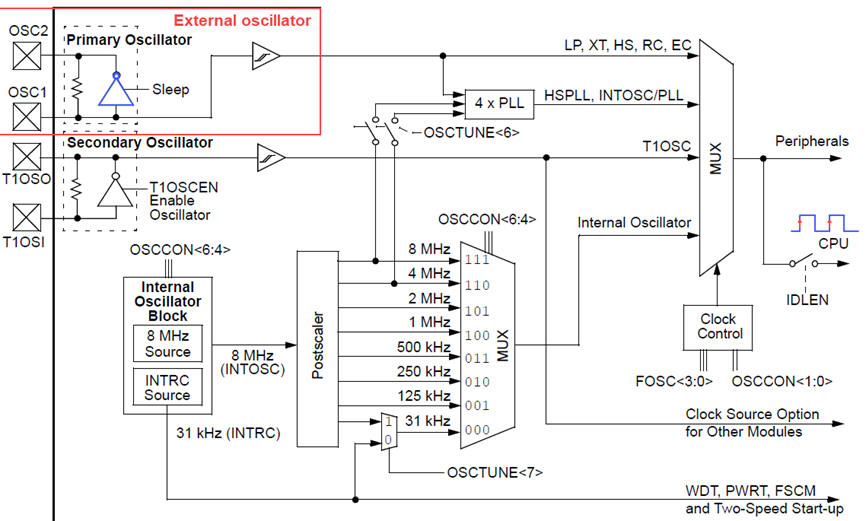
Fig. 9. PIC18F CLK options where an external quartz crystal can be wired between pins OSC1 and OSC2. |
|
DE10-Lite CLK circuit
This is the CLK chip populating the DE10-Lite board: Texas Instruments CDCEx937, flexible low power LVCMOS clock generator. The CDCE937 and CDCEL937 devices are modular PLL-based low cost, high-performance, programmable clock synthesizers, multipliers and dividers. They generate up to 7 output clocks from a single input frequency. Each output can be programmed in-system for any clock frequency up to 230 MHz,
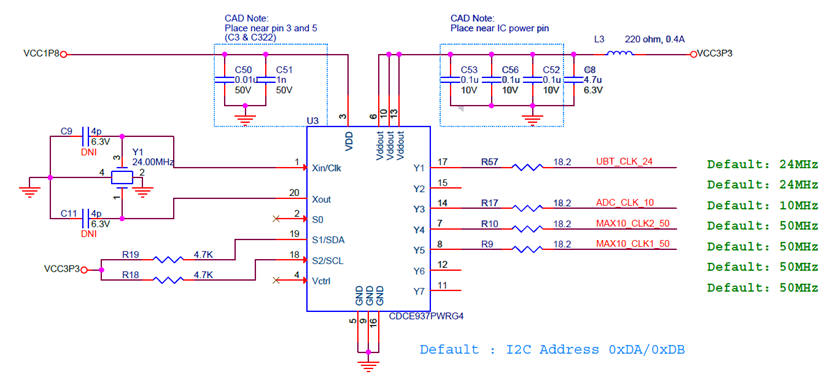  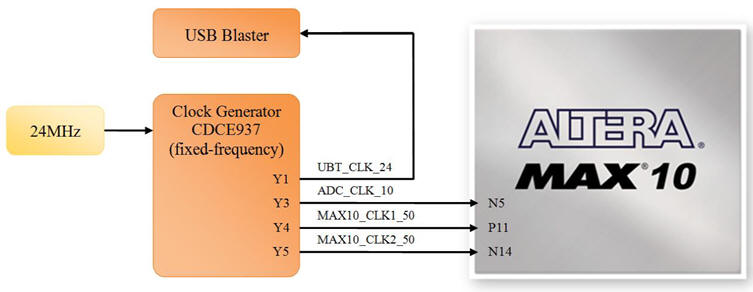 |
| Fig. 10. Details on DE10-Lite board CLK circuit. From a 24 MHz quartz crystal, the chip CDCE937 generates the three output CLK signals of 10 MHz, 24 MHz and 50 MHz. Two 50 MHz are available at the FPGA MAX10 at pins P11 and N14. |
News on the use of atomic clocks
Atomic clocks are so accurate that they will lose one second approximately every 100 million years. This is a news article on "After 84 Years, Canada Stops Broadcasting Time From Its Atomic Clocks", All About Circuits, 2023.