Chapter 1 problems |
- D1.10 - |
4-bit radix-2 /Johnson and 8-bit Johnson / radix-2 converters |
1.- Specifications of the 4-bit binari radix-2 to Johnson converter
Design the 4-bit binary radix-2 to Johnson code converter represented in Fig. 1.
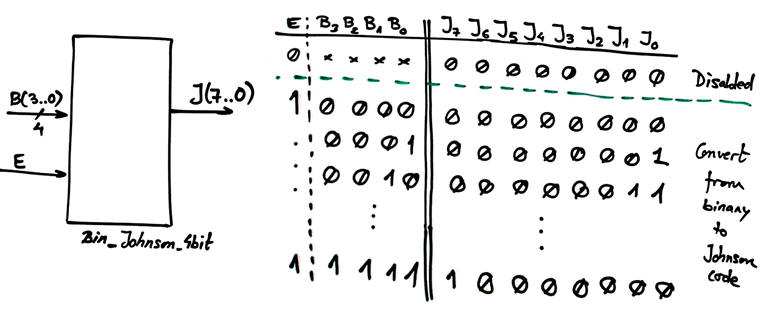 |
Fig.1. Symbol of the 4-bit binary to Johnson converter. |
Complete its truth table and answer questions such: How many maxterms contain J(6)? How many minterms contain J(1)?
Draw an example of timing diagram to be used later as stimulus in the VHDL testbench when verifying the synthesised circuit. Consider Min_Pulse = 2.78 ms.
The same project B3.10 is proposed in Chapter 3 for learning the basics of μC software organisation and basic digital I/O.
CPLD or FPGA target chip options:
Target option #1.: MAX II
Target option #2.: MAX 10
Target option #3.: Cyclone IV
2. Planning
Plan A structural circuit based on logic gates and equations in a single VHDL file. We have many strategies, for instance:
option #1: use minilog to obtain PoS.
Project location:
C:\CSD\P2\Bin_Johnson_4bit_PoS\(files)
How many FPGA resources (logic cells, logic elements, etc.) are used? What is the percentage of the target chip used in this design?
option #2: use minilog to obtain SoP.
Project location:
C:\CSD\P2\Bin_Johnson_4bit_SoP\(files)
How many FPGA resources (logic cells, logic elements, etc.) are used? What is the percentage of the target chip used in this design?
Plan B behavioural approach writing the truth table or the high-level description or algorithm in VHDL in a single file (flat).
Project location:
C:\CSD\P2\Bin_Johnson_4bit_B\(files)
How many FPGA resources (logic cells, logic elements, etc.) are used? What is the percentage of the target chip used in this design?
After having studied P4 tutorials, additional questions can be added to our report. For instance:
-
Perform a gate-level simulation to measure propagation delays in a given signal transition.
-
Deduce the worst-case propagation delay running the timing analiser tool and calculate the circuit's maximum frequency of operation for the target chip used in the design.
Chapter 1 problems |
- D1.10 - |
4-bit radix-2/Johnson and 8-bit Johnson / radix-2 converters |
1.- Specifications of the 8-bit Johnson to binari radix-2 converter
Design the 8-bit Johnson to binary radix-2 code converter represented in Fig. 1.
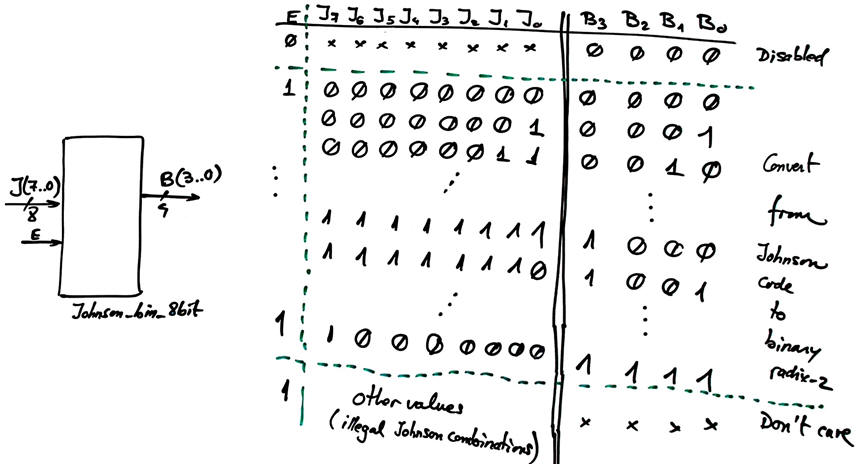 |
Fig.1. Symbol of the Johnson_bin_8bit converter. |
Complete the circuit's truth table and answer questions such: How many maxterms contain B(3)? How many minterms contain B(1)? IS it practical to design the circuit using its canonical equations? Where to find information on how to deal with incomplete functions? Can you add to the symbol and the truth table in Fig. 1 a new output such Error to be set high ('1') when the input presents an illegal Johnson code (as it was the case in the Tank_level_meter example)?
Draw an example of timing diagram to be used later as stimulus in the VHDL testbench when verifying the synthesised circuit. Consider Min_Pulse = 3.45 ms.
CPLD or FPGA target chip options:
Target option #1.: MAX II
Target option #2.: MAX 10
Target option #3.: Cyclone IV
2. Planning
Plan A structural circuit based on logic gates and equations in a single VHDL file. We have many strategies, for instance:
option #1: use minilog to obtain PoS.
Project location:
C:\CSD\P2\Johnson_bin_8bit_PoS\(files)
How many FPGA resources (logic cells, logic elements, etc.) are used? What is the percentage of the target chip used in this design?
option #2: use minilog to obtain SoP.
Project location:
C:\CSD\P2\Johnson_bin_8bit_SoP\(files)
How many FPGA resources (logic cells, logic elements, etc.) are used? What is the percentage of the target chip used in this design?
Plan B behavioural approach writing the truth table or the high-level description or algorithm in VHDL in a single file (flat).
Project location:
C:\CSD\P2\Johnson_bin_8bit_B\(files)
How many FPGA resources (logic cells, logic elements, etc.) are used? What is the percentage of the target chip used in this design?
Plan C2 is a hierarchical architecture based (multiple VHDL file) on components and signals.
For instance: using the method of decoders (MoD). Project location:
C:\CSD\P2\Johnson_bin_8bit_C2\MoD\(files)
Plan C2 is a hierarchical architecture based (multiple VHDL file) on components and signals.
For instance: using the method of memories (ROM). Project location:
C:\CSD\P2\Johnson_bin_8bit_C2\ROM\(files)
After having studied P4 tutorials, additional questions can be added to our report. For instance:
-
Perform a gate-level simulation to measure propagation delays in a given signal transition.
-
Deduce the worst-case propagation delay running the timing analiser tool and calculate the circuit's maximum frequency of operation for the target chip used in the design.


