|
L7.1: Counters [P7] Standard sequential blocks: Synchronous canonical counters |
[12/11] |
2.7. Standard synchronous sequential systems conceived and planned as FSM
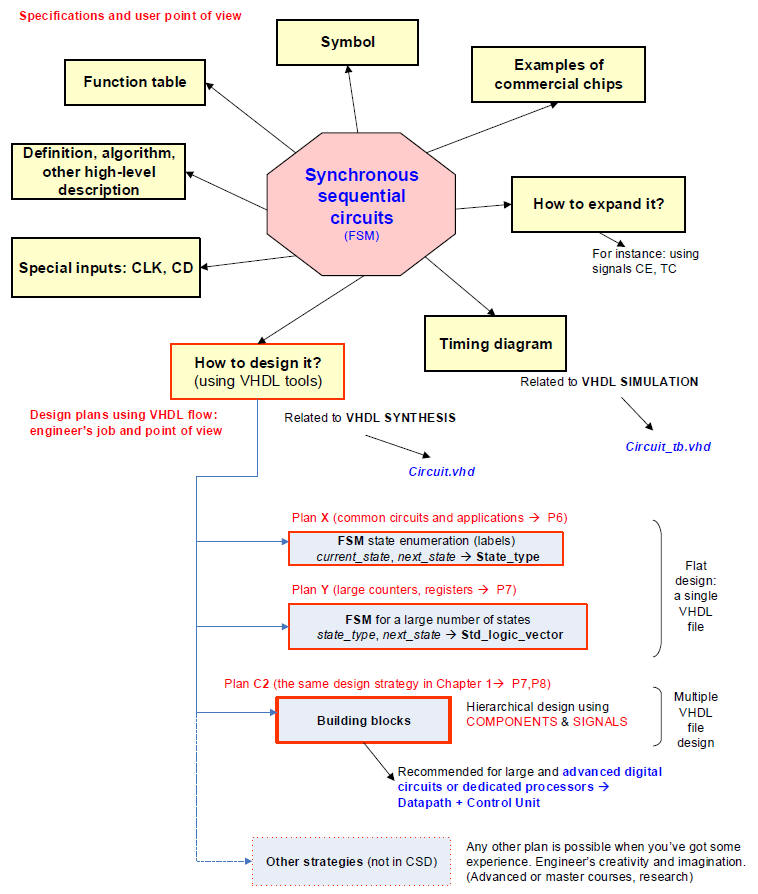
2.7.1. Concept map (pdf)(Visio)
2.7.2. Counters
2.7.2.1. Symbol, function table, modulo, timing diagram, state diagram, commercial chips
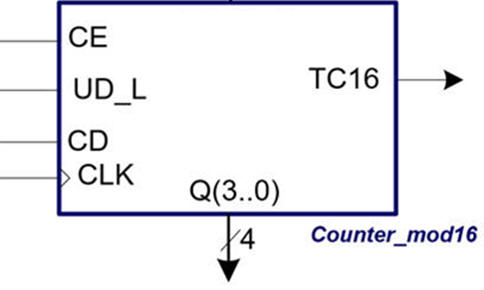
2.7.2.2. Control signals: count enable (CE), up and down (UD_L) or reversibility
2.7.2.3. Control signals: terminal count (TC) pulse
2.7.2.4. Output code:
2.7.2.4.1. Radix-2 (binary sequential)
2.7.2.4.2. BCD
2.7.2.4.3. One-hot or one-cold
2.7.2.4.4. Gray, Johnson, etc.
2.7.2.5. Design plan X: designing counters as FSM for small number of states and any output code (single-file plan C1 project) as an enumerated FSM like other examples in P6.
2.7.2.5.1. Example. Run the tutorial: Counter_BCD_1digit
A. Counter_mod12 not controlled (CLK, CD)
B. Counter_mod12 with counte enable (CE) and terminal count (TC12)
C. Counter_mod12 reversible (UD_L)
2.7.3. Radix-2 binary counters (Counter_modM), large number of states
2.7.3.1. Symbol, function table, modulo, timing diagram, state diagram, commercial chips
2.7.3.2. Additional control signal: parallel load (LD) or pre-setting output value
2.7.3.3. Design plan Y: designing counters using the VHDL arithmetic library and STD_LOGIC_VECTOR, single-file VHDL project
2.7.3.3.2. Example. Run the tutorial: Counter_BCD_1digit
2.7.3.3.3. Example: versatile/universal Counter_mod16
Comparison of alternative plans for designing counters. Counter_mod12 with parellel load (LD, Din)
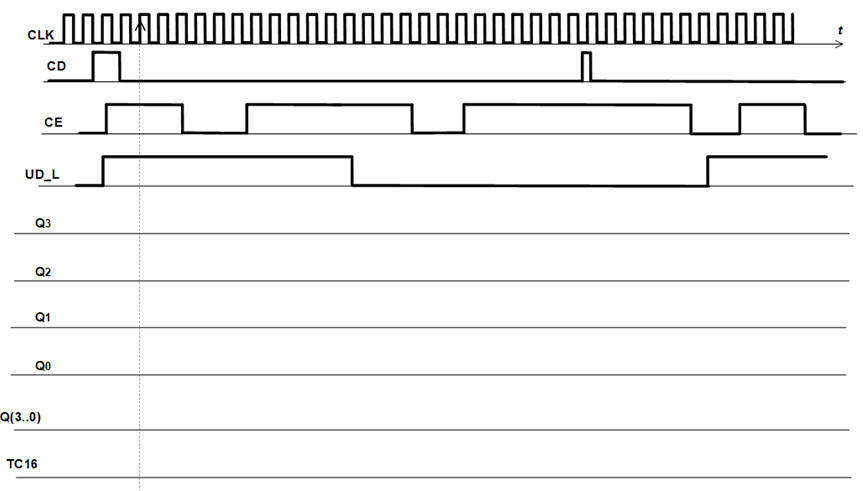
Exercise: Draw an example timing diagram (pdf) of the binary counter represented by its symbol and its function table.