|
|
||
|
|
Analysis of an asynchronous circuit |
|
|
|
||
LAB5 PROJECT PROPOSAL SAMPLE: Circuit_Async4
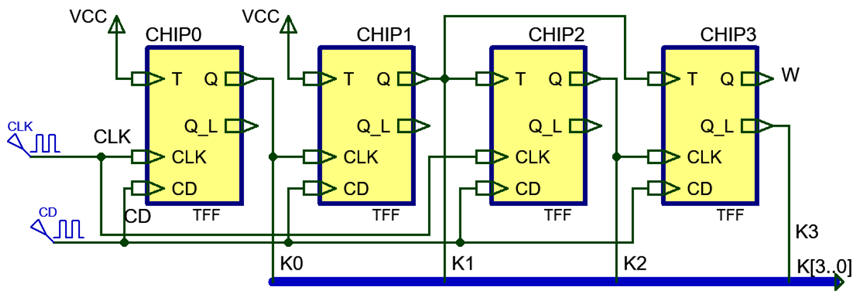
The circuit represented in Fig. 1 is composed of T_FF. Let us deduce how it works and what may be its application. This is an example of an asynchronous circuit that can serve to demonstrate how complicated and unreliable is asynchronous design compared to synchronous canonical design based on FSM that is presented in the next P6.
 |
|
Fig 1. Circuit_Async4 to be analysed using up to three methods. Draw this circuit in you own sheet of paper. |
Phase 1: analyse the T_FF memory cell component.
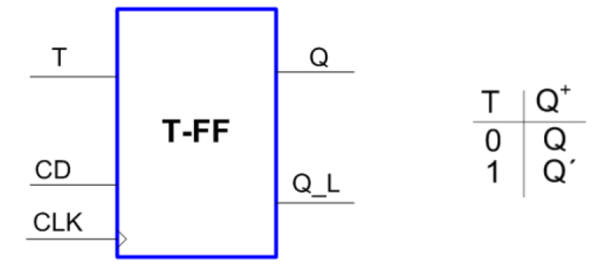
a) Analyse the behaviour of T_FF in Fig. 2 and represent the output Q in a timing diagram like the one represented in Fig.3.
 |
|
Fig 2. T_FF symbol, function table and state diagram. |
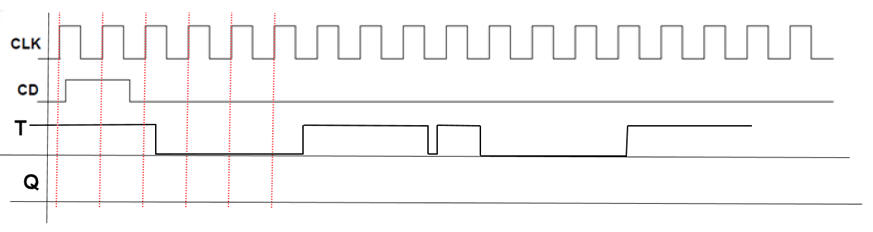
Indicate always the T sampled values using dots.
 |
|
Fig 3. Example input waveforms to be used as stimulus for calculating the output Q. |
Phase 2: circuit analysis. Three methods proposed.
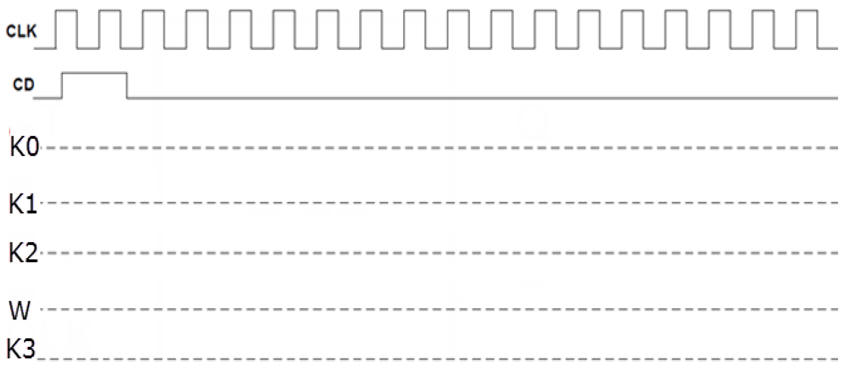
b) Method 1: Handwritten pen-and-paper analysis and discussion. Deduce the output Q(3..0) of the circuit represented in Fig. 1. The procedure is presented in P5 highlighted project.
 |
|
Fig 4. Waveforms. |
This method is developed in paper and results are verified by comparing with other methods.
Discuss how many states the system is capable of memorising.
Discuss what may be the function or application of the circuit. What is the circuit's main problem, so that it is not recommeded for precision applications?
This is an example of problem solution and discussion.
c) Method 2: using Proteus.
Capture Fig. 1 in Proteus and run simulations. For instance copy and adapt a similar structure such Proteus circuit based on CMOS classic chips. When picking parts from the library to mount your circuit, do this initialisation from Proteus top menu:
--> Tool --> Global Annotator --> Total.
Project location:
C:\CSD\P5\Circuit_Asyn4\
Print and discuss results from the logic analyser.
d) Method 3: using VHDL synthesis and simulation tools (plan C2 circuit).
Get the component T_FF model and translate to VHDL the top circuit (Circuit_Async3.vhd) to be able to start a new multiple-file plan C2 project.
Synthesise the project and print the RTL view. Be aware that the "number of registers" in the project's summary spreadsheet must be "4".
Use a VHDL test bench to demonstrate that the timing diagram looks like that obtained in Proteus or in the analysis above.
How can you observe and measure glitches, false states and complications around CLK transitions?
Optional: Alternative canonical circuit based on FSM.
e) Design an FSM that generates the same output K(3..0). It will be a better replacement of the asynchronous circuit in Fig. 1. Why?


