|
L3.1: Arithmetics in radix-2 [P3] Binary codes and radix-2 adders, comparators and multipliers |
[1/10] |
1.8. Binary codes and code converters
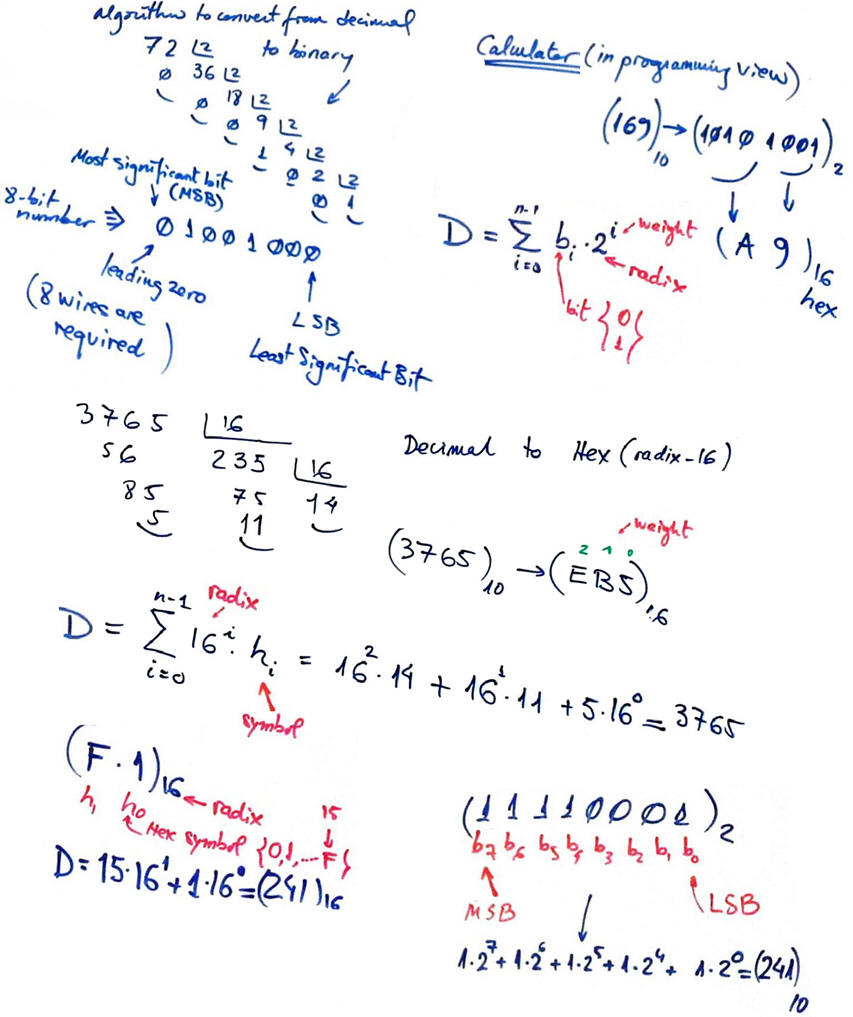
1.8.1. Number systems. Binary radix 2 (base 2), octal (base 8, hexadecimal (base 16)
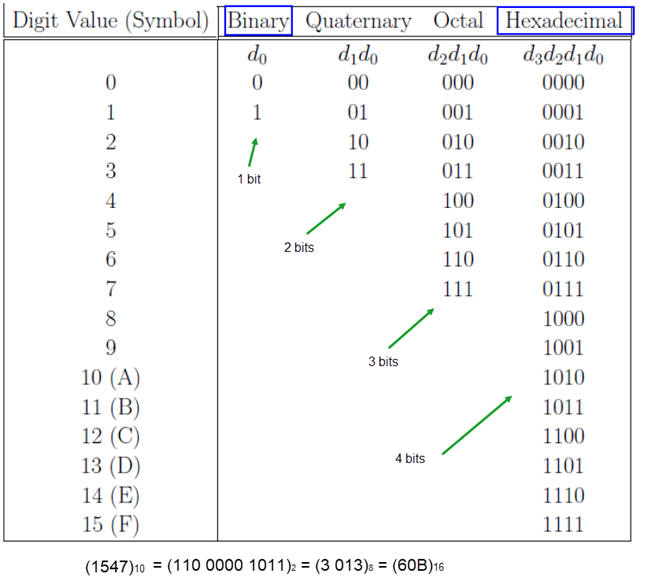
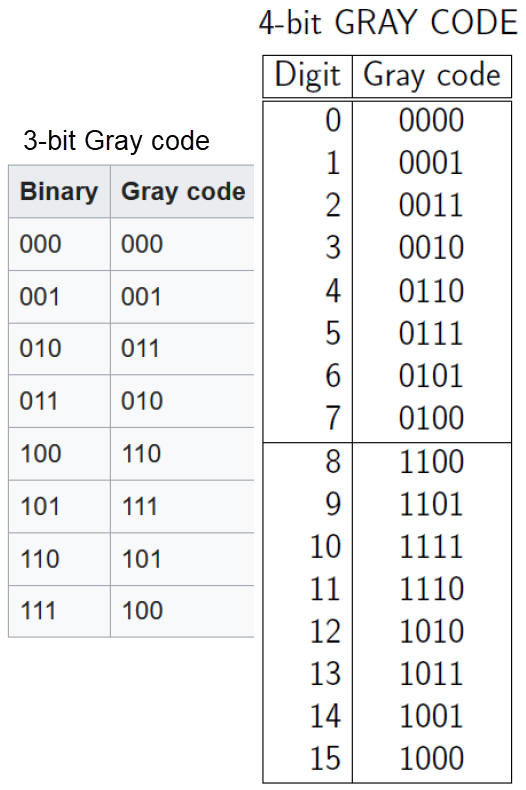
1.8.2. Gray code
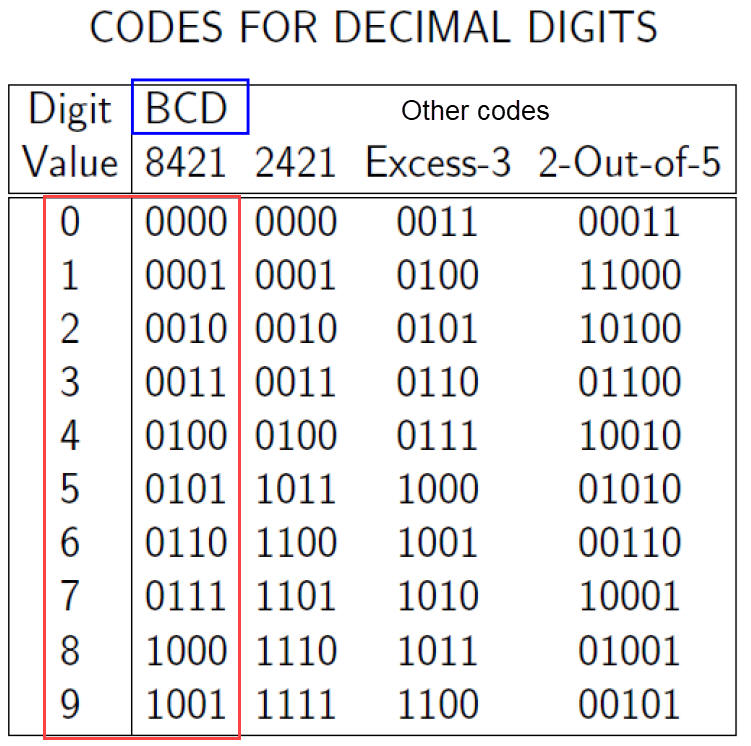
1.8.3. BCD (binary-coded decimal)
1.8.4. One-hot and one-cold
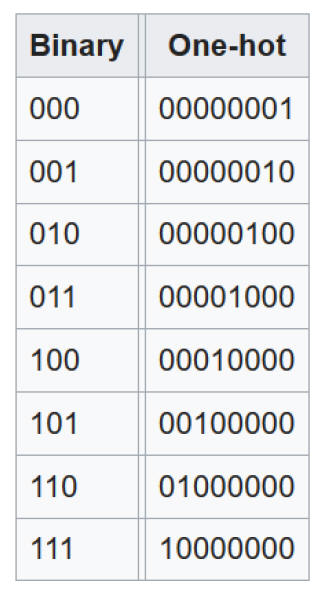
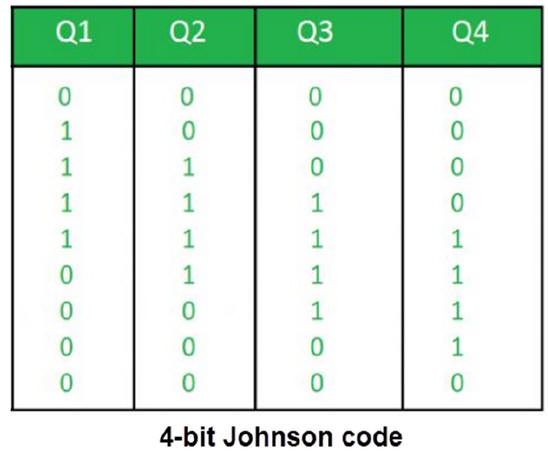
1.8.5. Johnson
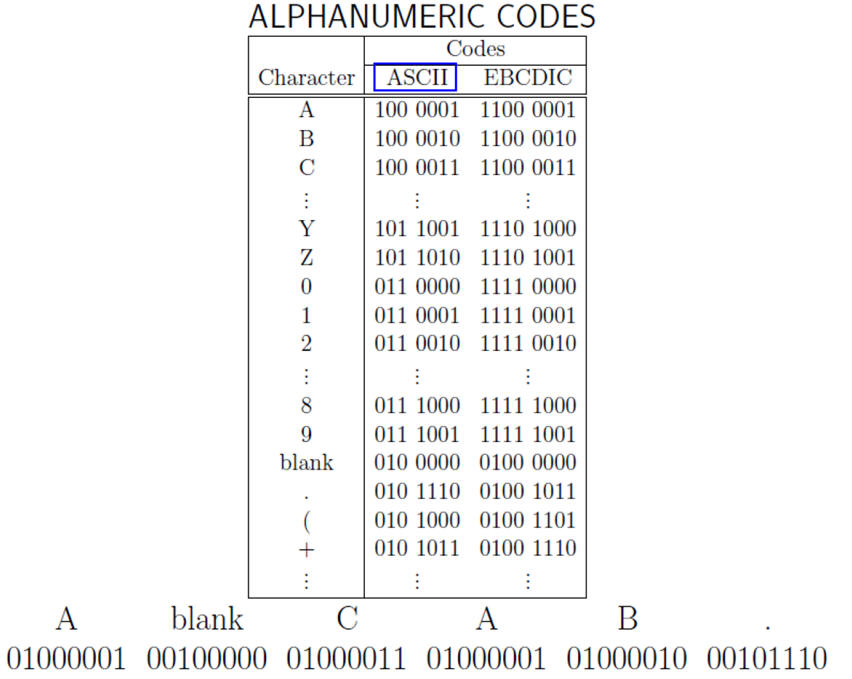
1.8.6. Keyboard symbols: ASCII, etc.
1.8.7. MORSE code. MORSE code translator.
1.8.8. Code converter circuits
1.8.8.1. Bin_BCD_converter_6bit
1.8.8.2. Gray_Bin_converter_4bit
1.9. Binary (radix-2, base-2) arithmetic circuits
1.9.1. Addition
1.9.1.1. 1-bit adder (Adder_1bit)
Binary numbers, symbols, range and how to perform additions.
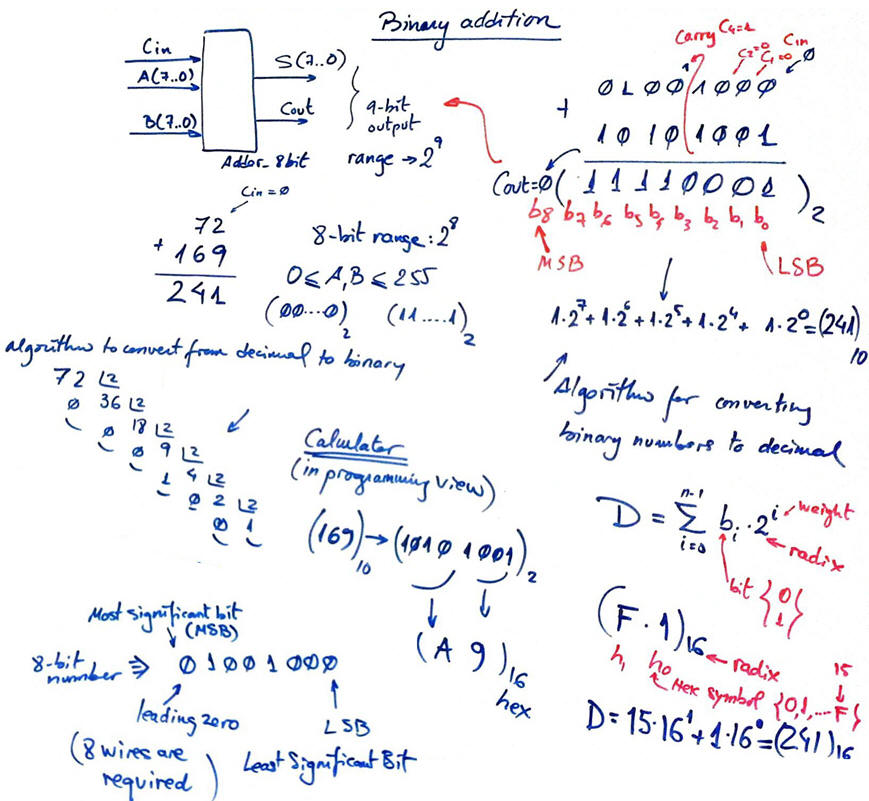
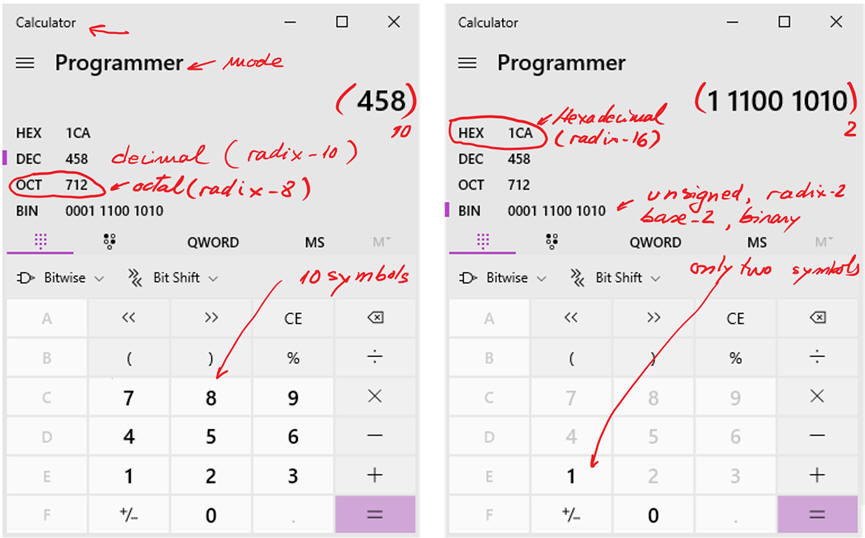
Conversion from binary to decimal, decimal to binary. Hexadecimal numbers. How to use the computer calculator in programming mode to work with bin/hex/oct/dec numbers.
Planning 1-bit expandable adders: tutorials on how to design the 1-bit full adder using our plans:
- Plan A: structural (equations) Adder_1bit
- Plan B: behavioural Adder_1bit
- Plan C2: Hierarchical multiple-file Adder_1bit
1.9.2. Comparator
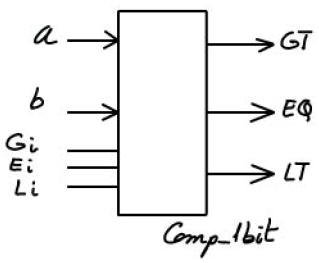
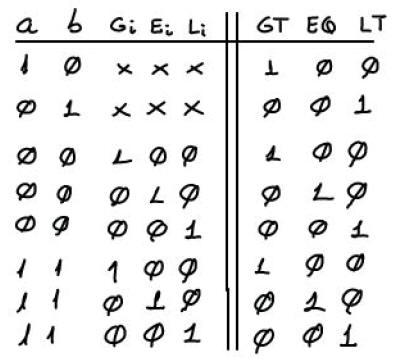
1.9.2.1. Expandable 1-bit comparator (Comp_1bit)
Symbol and truth table.
 |
 |
Planning expandable comparators:
- Plan A: 1-bit expandable comparator Comp_1bit
- Plan B: 1-bit expandable comparator Comp_1bit
- Plan C2: 1-bit expandable comparator Comp_1bit using the MoM
1.9.3. Multiplier
1.9.3.1. 1-bit multiplier cell, Mult_1bit
Exercise: Convert the following numbers and charecters:
(345)10 = ( )2 = ( )BCD = ( )16
10101)2 = ( )GRAY
10111)GRAY = ( )2 = ( )BCD
(1100001111010101010001001)2 = ( )16 = ( )BCD = ( )10
(6BFA87)16 = ( )2 = ( )BCD = ( )10
"Hello World 2024" = ( )ASCII = ( )MORSE


